Architecture
Architecture Overview of BIRT
BIRT has two main components:
- a report designer based on Eclipse, and
- a runtime component that you can add to your app server.
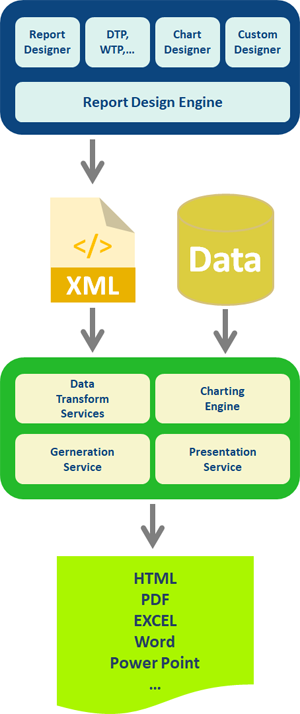
The Anatomy of a Report
BIRT reports consist of four main parts: data, data transforms, business logic and presentation.
Data - Databases, web services, Java objects all can supply data to your BIRT report. BIRT provides JDBC, XML, Web Services, and Flat File support, as well as support for using code to get at other sources of data. BIRT's use of the Open Data Access (ODA) framework allows anyone to build new UI and runtime support for any kind of tabular data. Further, a single report can include data from any number of data sources. BIRT also supplies a feature that allows disparate data sources to be combined using inner and outer joins.
Data Transforms - Reports present data sorted, summarized, filtered and grouped to fit the user's needs. While databases can do some of this work, BIRT must do it for "simple" data sources such as flat files or Java objects. BIRT allows sophisticated operations such as grouping on sums, percentages of overall totals and more.
Business Logic - Real-world data is seldom structured exactly as you'd like for a report. Many reports require business-specific logic to convert raw data into information useful for the user. If the logic is just for the report, you can script it using BIRT's JavaScript support. If your application already contains the logic, you can call into your existing Java code.
Presentation - Once the data is ready, you have a wide range of options for presenting it to the user. Tables, charts, text and more. A single data set can appear in multiple ways, and a single report can present data from multiple data sets.
BIRT Components
The BIRT project delivers many components. These are listed below with a brief description. More information about BIRT components and architecture is available in the documentation section.
BIRT Report Designer - The BIRT Report Designer is an Eclipse perspective that is used to create BIRT report designs. These designs are stored in an open XML format. The Designer can be downloaded as a Rich Client Platform (RCP) application, a set of plug-ins to enable the Designer perspective within an existing Eclipse build or as an all in one download that includes Eclipse.
Design Engine - This engine is responsible for creating and modifying report designs. The Design Engine API (DE API) wraps the functionality of the design engine and is available for use within any Java/Java EE project. The BIRT Report Designer uses this API internally to construct the XML designs.
Report Engine - The Report Engine uses the report design files to generate and render reports. Using the Report Engine API (RE API) the engine can be embedded within any Java/Java EE application. The BIRT Web Viewer uses this API to execute and display reports.
Charting Engine - The Charting Engine is used to design and generate Charts either in standalone or embedded within BIRT reports. The Charting Engine API (CE API) allows Java/Java EE developers to add charting capabilities to their applications. The Design and Report Engines make use of this API to deliver Charts.
BIRT Viewer - The BIRT project provides a sample "viewer" that is used to preview reports within Eclipse. BIRT includes an Apache Tomcat server invoked each time you preview your report. In addition to being packaged as an Eclipse Plug-in, the Viewer is also available as a standalone Java EE application, which can be used in any JSP-compliant Java EE server. The Viewer Plug-in can also be embedded within a Rich Client Platform (RCP) application. BIRT provides web output as a single HTML document, paginated HTML, PDF, XLS, DOC, PPT, and Postscript. Additionally the viewer allows exporting the data to CSV, printing, and Table of Contents functionality.